Before we plunge into the realm of USB4, let’s take a quick trip down memory lane. USB, or Universal Serial Bus, has been the backbone of peripheral connectivity for over two decades. From humble beginnings with USB 1.0 to the lightning-fast speeds of USB 3.2, this ubiquitous interface has evolved to meet the ever-growing demands of modern computing.
USB (with an “A” connector)
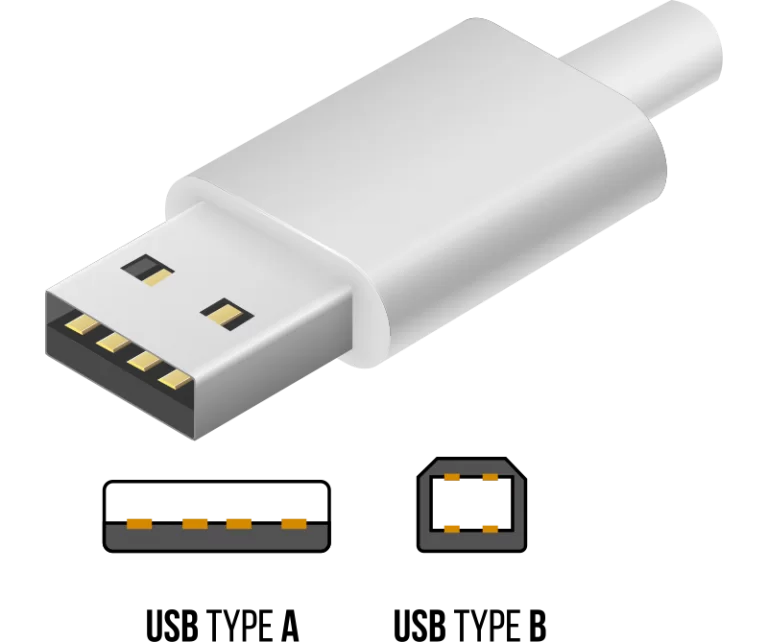

USB 1.0, the groundbreaking interface that revolutionized connectivity! USB 1.0, standing for Universal Serial Bus, brought about a new era of plug-and-play simplicity to computing. Let’s dive into its features and specifications:
Speed: USB 1.0 introduced a data transfer rate of up to 1.5 Mbps (megabits per second). This speed was a significant leap from previous interfaces, such as serial and parallel ports, offering faster data transmission for a range of devices.
Compatibility: One of the standout features of USB 1.0 was its universal compatibility. It allowed for the connection of various peripherals, including keyboards, mice, printers, scanners, and storage devices, without the need for specialized ports or adapters. This universality simplified the user experience and streamlined the setup process for peripherals.
Hot Swapping: USB 1.0 introduced the concept of hot swapping, enabling users to connect and disconnect devices without shutting down the computer. This feature provided greater flexibility and convenience, allowing users to easily add or remove peripherals on the fly.
Power Delivery: USB 1.0 also introduced a power delivery mechanism, providing up to 5 volts of power to connected devices. This feature eliminated the need for separate power adapters for many peripherals, reducing clutter and simplifying setup.
Plug-and-Play: With USB 1.0, gone were the days of complicated driver installations and configuration settings. The plug-and-play functionality allowed compatible devices to be automatically detected and configured by the operating system, making the setup process hassle-free for users.
Backward Compatibility: Despite being the first iteration of the USB standard, USB 1.0 maintained backward compatibility with older devices and ports. This ensured that users could continue to use their existing peripherals while transitioning to the new standard, without the need for costly upgrades.
Connectors: The Type-A and Type-B connectors came in Standard, Mini, and Micro sizes. The standard format was the largest and was mainly used for desktop and larger peripheral equipment. The Mini-USB connectors (Mini-A, Mini-B, Mini-AB) were introduced for mobile devices, but they were quickly replaced by the thinner Micro-USB connectors (Micro-A, Micro-B, Micro-AB). The Type-C connector, also known as USB-C, is not exclusive to USB, is the only current standard for USB and is required for USB4. Other standards use it as well as well, including modern DisplayPort and Thunderbolt. It is reversible and can support various functionalities and protocols including USB; some are mandatory, many optional, depending on the type of the hardware: host, peripheral device, or hub.
Overall, USB 1.0 laid the foundation for modern connectivity, offering a combination of speed, compatibility, and convenience that transformed the way we interact with our computers and peripherals. It set the stage for future iterations of the USB standard, paving the way for even faster data transfer rates and expanded functionality.
USB 2.0
USB 2.0 took the connectivity game to a whole new level, offering improved speed and functionality over its predecessor. Let’s delve into the differences:
Speed: USB 2.0 ramped up the data transfer rate to a staggering 480 Mbps (megabits per second), a significant leap from the 1.5 Mbps offered by USB 1.0. This blazing-fast speed opened up new possibilities for high-speed data transfer, making tasks such as transferring large files and streaming multimedia content smoother and more efficient.
Compatibility: Like USB 1.0, USB 2.0 maintained universal compatibility with a wide range of devices. It continued to support peripherals such as keyboards, mice, printers, scanners, and storage devices, ensuring seamless connectivity across different hardware platforms.
Backward Compatibility: USB 2.0 retained backward compatibility with USB 1.0 devices and ports. This meant that users could still use their existing peripherals with the new standard, without the need for costly upgrades or adapters. The backward compatibility ensured a smooth transition to the faster USB 2.0 standard.
Power Delivery: USB 2.0 maintained the power delivery mechanism of its predecessor, providing up to 5 volts of power to connected devices. This feature eliminated the need for separate power adapters for many peripherals, reducing clutter and simplifying setup.
Enhanced Performance: With its higher data transfer rate, USB 2.0 offered enhanced performance for a wide range of applications. It enabled smoother data streaming, faster file transfers, and improved responsiveness for connected devices, enhancing the overall user experience.
USB 3.0, 3.1, 3.2
- Speed: USB 3.0, also known as SuperSpeed USB, introduced a substantial boost in data transfer rates compared to its predecessors. It offered a maximum transfer rate of up to 5 Gbps (gigabits per second), which is approximately ten times faster than USB 2.0.
- Backward Compatibility: USB 3.0 maintained backward compatibility with USB 2.0 devices and ports, ensuring seamless connectivity with existing peripherals.
- Increased Power: USB 3.0 enhanced power delivery capabilities, allowing for faster charging of devices and providing more power to connected peripherals.
USB 3.1:
- Speed: USB 3.1, also known as SuperSpeed+ USB, further pushed the boundaries of data transfer speeds. It doubled the maximum transfer rate to up to 10 Gbps, offering even faster performance for high-bandwidth applications.
- Enhanced Power Delivery: USB 3.1 introduced improvements in power delivery, enabling faster charging of devices and supporting higher power requirements for connected peripherals.
- Reversible Connector: USB 3.1 Type-C connectors were introduced, featuring a reversible design that could be plugged in either way, making it more convenient and user-friendly.
Rugged connector options:

USB 3.2:
- Speed: USB 3.2 continued the trend of increasing data transfer speeds. It doubled the maximum transfer rate once again, offering speeds of up to 20 Gbps, making it ideal for demanding applications such as high-resolution video streaming and data-intensive gaming.
- Enhanced Compatibility: USB 3.2 maintained backward compatibility with previous USB generations, ensuring that users could continue to use their existing peripherals with the new standard.
- Improved Efficiency: USB 3.2 introduced more efficient data encoding techniques, further optimizing data transfer speeds and reducing latency for faster and more responsive performance.
The USB4 Revolution
Enter USB4, the latest iteration of the USB standard poised to revolutionize the way we connect and interact with our devices. Announced by the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF) in 2019, USB4 represents a significant leap forward in terms of speed, versatility, and compatibility.
At its core, USB4 builds upon the foundation laid by Thunderbolt 3, incorporating many of its features and capabilities. This includes blazing-fast data transfer speeds of up to 40Gbps, support for multiple display protocols, and the ability to daisy-chain devices for seamless connectivity.
Key Features
So, what sets USB4 apart from its predecessors? Here are some key features that make it a game-changer:
- Speed and Bandwidth: With USB4, users can experience lightning-fast data transfer speeds of up to 40Gbps, doubling the maximum throughput of USB 3.2 Gen 2×2. Whether you’re transferring large files, streaming 4K video, or gaming online, USB4 ensures smooth and efficient performance.
- Backward Compatibility: Despite its impressive speed capabilities, USB4 remains backward compatible with previous USB generations, ensuring seamless connectivity with existing devices. Whether you’re plugging in a USB2.0 flash drive or a USB3.2 external hard drive, USB4 has you covered.
- Power Delivery: USB4 supports USB Power Delivery (USB-PD), allowing for fast charging of compatible devices. With USB-PD, you can charge your smartphone, tablet, or laptop more quickly and conveniently than ever before, eliminating the need for bulky power adapters.
- Display Support: USB4 offers native support for multiple display protocols, including DisplayPort and HDMI, enabling users to connect external monitors, TVs, and projectors with ease. Whether you’re extending your desktop workspace or enjoying multimedia content on a larger screen, USB4 delivers stunning visuals without compromise.
Rugged version of the connectors:

The Future of Connectivity
As we embrace the era of USB4, the possibilities for innovation and collaboration are endless. Whether you’re a gamer seeking the fastest speeds for your peripherals, a content creator in need of reliable data transfer, or a professional looking to streamline your workflow, USB4 opens doors to a world of possibilities.
So, whether you’re upgrading your laptop or lunchbox with the latest USB4 ports or investing in peripherals that harness its power, rest assured that USB4 is poised to shape the future of connectivity for years to come.